Interactive RBR - Guide Page IV: 18 Months - 5 Years
- Home
- Guide Page IV: 18 Months - 5 Years
The Interactive RBR provides the evidence and resources for the items in the RBR.
Clicking on any item with blue shading reveals:
- Evidence summary: Summary of current evidence on this item as outlined in RBR Resource Pages 1 – 4. One can link to guidelines and parent resources organized by topic.
- Parent resources: web links to reliable resources on this item.
Growth
|
Healthy bodies for children and teens - Dietitians of Canada
Feeding Infants and Toddlers - Dietitians of Canada
Finding and Keeping a Healthy Body Weight - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
Download WHO Growth Charts for Canada - Dietitians of Canada
Breastfeeding: How do you know your baby is getting enough milk? - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Breastfeeding learning hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth.
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/breastfeeding
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding: Exclusive breastfeeding is recommended for the first six months of life for healthy term infants. Introduction of solids should be led by the infant's signs of readiness-a few weeks before to just after 6 months. Breast milk is the optimal food for infants, and breastfeeding (with complementary foods) may continue for up to two years and beyond unless contraindicated. Breastfeeding may reduce gastrointestinal and respiratory infections and helps to protect against SIDS. Maternal support (both antepartum and postpartum) increases breastfeeding and prolongs its duration. Early and frequent mother- infant contact, rooming in, and banning handouts of free infant formula increase breastfeeding rates.
|
Nutrition for Healthy Term Infants Birth to 6 Months – Health Canada
Feeding Infants and Toddlers - Dietitians of Canada
Drugs and Lactation Database (TOXNET) - A peer-reviewed and fully referenced database of drugs to which breastfeeding mothers may be exposed - National Institute of Health
Breastfeeding - Canadian Paediatric Society - Caring for Kids
Breastfeeding - La Leche League Canada
Breastfeeding and Infant Nutrition - Public Health Agency of Canada
Breastfeeding: How do you know your baby is getting enough milk? - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Breastfeeding Your Baby – More Information - Baby Friendly NL, Health Canada
Breastfeeding problems: Sore nipples - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
My Food Guide Serving Tracker for Breastfeeding Women - Health Canada
Thrush - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Vitamin D Supplementation and Breastfeeding - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Pacifiers (Soothers) : A User’s Guide for Parents - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Pediatric Nutrition Guidelines (Birth to Six Years) for Health Professionals - Ontario Dietitians in Public Health (ODPH)
Weaning Your Child From Breastfeeding - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Breastfeeding: Weaning and withdrawing your milk supply - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Feeding Your Baby in the First Year - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Medications, alcohol and cannabis in breastfeeding - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth. https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=442&language=English
Breastfeeding learning hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth.
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/breastfeeding
Caring for Kids New to Canada - Canadian Paediatric Society. https://www.kidsnewtocanada.ca/
Your Newborn: Bringing Baby Home - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Vitamin D Supplementation
Vitamin D supplementation of 400 IU/day (800 IU/day in high-risk infants) is recommended for infants/children for as long as they are breastfed. Breastfeeding mothers should consume a standard multivitamin/mineral supplement that contains vitamin D (400 IU/day). |
Nutrition for Healthy Term Infants Birth to 6 Months – Health Canada
Breastfeeding and Infant Nutrition - Public Health Agency of Canada
Breastfeeding Your Baby – More Information - Baby Friendly NL, Health Canada
Vitamin D Supplementation and Breastfeeding - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Pediatric Nutrition Guidelines (Birth to Six Years) for Health Professionals - Ontario Dietitians in Public Health (ODPH)
Feeding Your Baby in the First Year - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Breastfeeding learning hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth.
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/breastfeeding
Caring for Kids New to Canada - Canadian Paediatric Society. https://www.kidsnewtocanada.ca/
Formula Feeding
|
Pediatric Nutrition Guidelines (Birth to Six Years) for Health Professionals - Ontario Dietitians in Public Health (ODPH)
Weaning Your Child From Breastfeeding - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Feeding Your Baby in the First Year - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Breastfeeding learning hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth.
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/breastfeeding
Behaviour and Family Issues
Disruptive behaviour (CPS/CACAP) Refer parents of children at risk of, or showing signs of, behavioural or conduct problems to structured parenting programs which have been shown to increase positive parenting, improve child compliance, and reduce general behaviour problems. Access community resources to determine the most appropriate and available research-structured programs. Parenting skills (EECD) |
Colic and Crying - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Taming the Monsters: Helping Children Deal with their Fears - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Night Terrors - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Positive discipline for young children - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Tips for positive parenting and managing behaviour in children up to age 5 - AboutKidsHealth – Caring for Kids
What's the Best Way to Discipline My Child? - American Academy of Pediatrics - healthychildren.org
Helping Children Cope with Separation and Divorce - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Helping children and teens cope with stressful public events - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Dental Care for Children – Pacifiers and Thumb Sucking - Canadian Dental Association
Bedwetting - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Bed-Wetting (Enuresis) - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Say Goodbye to Picky Eating - Dietitians of Canada - UnlockFood.ca. https://www.unlockfood.ca/en/Articles/Child-Toddler-Nutrition/Say-Goodbye-to-Picky-Eating!.aspx
Sleep: Learning Hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/SLEEP
Biting in Childcare : What are the Risks? - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
How to Foster your Child’s Self Esteem - CPS - Caring for Kids
Transportation in motor vehicles
Transportation in motorized vehicles including cars, ATVs, snowmobiles, etc.:
|
Car Seat Safety - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Car Seats - Parachute Canada
Choosing the right car seat - Parachute Canada
Car seats: Other ways to travel - Parachute Canada
All-Terrain Vehicle Safety - Parachute Canada
Are ATVs safe for children and youth? - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Snowmobiles: Safety Tips for Families - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Cycling: Child carriers and trailers - Parachute Canada
Keep your young child safe around the house - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Heat-related Illness: How to Prevent - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=1966&language=English
Prevent Child Deaths in Hot Cars - American Academy of Pediatrics - healthychildren.org https://www.healthychildren.org/English/safety-prevention/on-the-go/Pages/Prevent-Child-Deaths-in-Hot-Cars.aspx
Helmets: How they Prevent Injury - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=1982&language=English
Your Newborn: Bringing Baby Home - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Carbon Monoxide / Smoke Detectors
Burns: Install smoke detectors in the home on every level. Keep hot water at a temperature < 49oC. Be vigilant with hot liquids on counter-tops. |
Sun Safety - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Sunburn - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Sun: Protecting Your Child’s Skin - The Hosptial for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Burns and scalds - Parachute Canada
Preventing burns: Winter safety - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Burns: Learning hub - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Preventing Burns: Campfires and Fireworks - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Burns: Household Safety and Prevention - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Poisons
Poisons and other toxins: Keep medicines and cleaners, and other toxic substances locked up and out of child’s reach. Have Poison Control Centre number (PCC#) handy. Use of ipecac is contraindicated in children. Install carbon monoxide detectors. |
Food Poisoning: Protecting Your Family - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Food Safety for Pregnant Women - Health Canada – It’s Your Health
Food Safety at Home - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Poisoning - Parachute Canada
Poison Information Centers in Canada - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Poison-Proof Your Home: A Guide to Keeping Your Family Safe From Poisons - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Lead Poisoning - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Keep your young child safe around the house - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Antimicrobial Products in the Home - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Firearm safety
| Firearm safety: Advise on removal of firearms from home or safe storage to decrease risk of unintentional firearm injury, suicide, or homicide. Prevention of firearm injuries (CPS) |
Keep your young child safe around the house - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Gun Safety: Information for Families - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Bath Safety
Drowning: Prevention of drowning (AAP)
|
Drowning - Parachute Canada
Water Safety for Young Children - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Water safety and drowning prevention - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Bathtub Safety - Parachute Canada
Keep your young child safe around the house - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Drowning: Play parks and water features - Parachute Canada
Drowning: Backyard pools - Parachute Canada https://www.parachutecanada.org/en/injury-topic/drowning/backyard-pools/
Drowning: Lifejackets and PFDs - Parachute Canada https://www.parachutecanada.org/en/injury-topic/drowning/lifejackets-and-personal-flotation-devices-pfds/
Choking
Choking: Avoid hard, small and round, smooth, and sticky solid foods until age 4 years. Encourage child to remain seated while eating and drinking. Use safe toys, follow minimum age recommendations, and remove loose parts and broken toys. Preventing choking and suffocation in children (CPS) |
Halloween Safety - Health Canada – It’s Your Health
Choking - Parachute Canada
Choking: First Aid - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Keep your young child safe around the house - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Pacifer Use
Pacifier use: Counsel on safe and appropriate use. Pacifiers may decrease risk of SIDS and should not be discouraged in the 1st year of life after breastfeeding is well established, but should be restricted in children with chronic/recurrent otitis media. Recommendations for pacifier use (CPS) |
Pacifiers (Soothers) : A User’s Guide for Parents - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Dental Care for Children – Pacifiers and Thumb Sucking - Canadian Dental Association
Safe Sleeping
Safe sleeping environment: Joint statement (CPS/CFSIDS/CICH/HC/PHAC) | 2016 task force on SIDS (AAP)
|
Pacifiers (Soothers) : A User’s Guide for Parents - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Safe Sleep for Babies - Canadian Pediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Preventing Flat Heads in Babies Who Sleep on Their Backs - Canadian Pediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Healthy Sleep for your Baby and Child - Canadian Pediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Safe Sleep for Your Baby - Public Health Agency of Canada
Home Safety: Bed Time - Parachute Canada
Sleeping Problems - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Keep your young child safe around the house - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Tummy time: Helping your baby - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=296&language=English
Sleep: Learning Hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/SLEEP
Industry Guide for the Classification of Cribs, Cradles, Bassinets and Related Products - Health Canada https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/consumer-product-safety/reports-publications/industry-professionals/industry-guide-classification-cribs-cradles-bassinets-related-products.html
Falls
Falls: Assess home for hazards – never leave baby alone on change table or other high surface; use window guards and stair gates. Baby walkers are banned in Canada and should never be used. Ensure stability of furniture and TV. Advise against trampoline use at home. Trampoline safety (AAP) |
Are Trampolines Safe? - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Keep your young child safe around the house - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Unstructured outdoor play and risky play - Parachute Canada https://www.parachutecanada.org/en/injury-topic/playgrounds-and-play-spaces/unstructured-outdoor-play-and-risky-play/
Head Injury and concussion - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=766&language=English
Crying
Crying: Excessive crying may be caused by behavioural or physical factors or be the upper limit of the normal spectrum. Caregiver frustration with infant crying can lead to child maltreatment/inflicted injury (head injury, fractures, bruising). The Period of Purple Crying. |
Colic and Crying - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Night Waking
Night waking: Occurs in 20% of infants and toddlers who do not require night feeding. Counselling around positive bedtime routines (including training the child to fall asleep alone), removing nighttime positive reinforcers, keeping morning awakening time consistent, and rewarding good sleep behaviour has been shown to reduce the prevalence of night waking, especially when this counselling begins in the first 3 weeks of life. Behaviour modification & sleep (MJA) Sleep problems & night wakings (Sleep) |
Safe Sleep for Babies - Canadian Pediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Healthy Sleep for your Baby and Child - Canadian Pediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Safe Sleep for Your Baby - Public Health Agency of Canada
Sleeping Problems - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Night Terrors - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Bed-Wetting (Enuresis) - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Sleep: Learning Hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/SLEEP
Parenting/Discipline
Supporting Positive parenting (CPS) Inform parents that warm, responsive, flexible, and consistent discipline techniques are associated with positive child outcomes. Over reactive, inconsistent, cold, and coercive techniques are associated with negative child outcomes. Use of any physical punishment including spanking should be discouraged in all ages. Effective discipline for children (PCH) Refer parents of children at risk of, or showing signs of, behavioural or conduct problems to structured parenting programs which have been shown to increase positive parenting, improve child compliance, and reduce general behaviour problems. Access community resources to determine the most appropriate and available research-structured programs. Parenting skills (EECD) |
Taming the Monsters: Helping Children Deal with their Fears - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Positive discipline for young children - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Tips for positive parenting and managing behaviour in children up to age 5 - AboutKidsHealth – Caring for Kids
What's the Best Way to Discipline My Child? - American Academy of Pediatrics - healthychildren.org
Helping Children Cope with Separation and Divorce - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Helping children and teens cope with stressful public events - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Say Goodbye to Picky Eating - Dietitians of Canada - UnlockFood.ca. https://www.unlockfood.ca/en/Articles/Child-Toddler-Nutrition/Say-Goodbye-to-Picky-Eating!.aspx
Early language development in babies and toddlers - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/early-language-development-in-babies-and-toddlers?language=en
Babbling with your child - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=3895&language=English
Tips for developing language at 3 years - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=3897&language=English
Sensory development and activities for children older than 2 years - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=3890&language=English
Spatial reasoning skills: How to foster in children - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=649&language=English
Biting in Childcare : What are the Risks? - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
How to Foster your Child’s Self Esteem - CPS - Caring for Kids
Parental Fatigue / Postpartum Depression
Maternal depression: Physicians should have a high awareness of maternal depression, which is a risk factor for the socio-emotional and cognitive development of children. Although less studied, paternal factors may compound the maternal-infant issues. Maternal depression and child development (CPS) |
Social determinants of health (SDH): Inquiry about impact of poverty: “Within the past 12 mos, did you worry that your food would run out before you got money to buy more, OR did the food not last and you didn’t have money to get more?” Food insecurity (Pediatrics) | CLEAR tool kit | Poverty Tool (OCFP) | Social determinants of health (CFPC) | Infrastructure to address SDH (PCH) |
Prevention of child maltreatment:
Discuss with parents of preschoolers teaching names of genitalia, appropriate and inappropriate touch, and normal sexual behaviour for age. Exposure to personal violence and other forms of violence has significant impact on physical and emotional well-being of children. Assess home visit need: There is good evidence for home visiting by nurses during the perinatal period through infancy for first-time mothers of low socioeconomic status, single parents or teenaged parents to prevent physical abuse and/or neglect. |
High Risk
Maternal depression: Physicians should have a high awareness of maternal depression, which is a risk factor for the socio-emotional and cognitive development of children. Although less studied, paternal factors may compound the maternal-infant issues. Maternal depression and child development (CPS) Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD). Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (AAP) Adoption/Foster care: Children newly adopted or entering foster care are a high risk population with special needs for health supervision. Foster Care (CPS) | International Adoption: Preparing to adopt | International Adoption: Enhancing attachment Immigrants/refugees: Caring for kids new to Canada (CPS) | CCIRH-Clinical Guidelines | Cross-cultural communication (CPS) Aboriginal children: Social determinants of health in Aboriginal children in Canada (PCH) Social determinants of health (SDH): Inquiry about impact of poverty: “Within the past 12 mos, did you worry that your food would run out before you got money to buy more, OR did the food not last and you didn’t have money to get more?” Food insecurity (Pediatrics) | CLEAR tool kit | Poverty Tool (OCFP) | Social determinants of health (CFPC) | Infrastructure to address SDH (PCH) Prevention of child maltreatment:
Assess home visit need: There is good evidence for home visiting by nurses during the perinatal period through infancy for first-time mothers of low socioeconomic status, single parents or teenaged parents to prevent physical abuse and/or neglect. |
Colic and Crying - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Keep your young child safe around the house - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Positive discipline for young children - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Tips for positive parenting and managing behaviour in children up to age 5 - AboutKidsHealth – Caring for Kids
What's the Best Way to Discipline My Child? - American Academy of Pediatrics - healthychildren.org
Depression in Pregnant Women and Mothers: How it affects you and your child - Canadian Pediatric Society – Caring for Kids
A Parent’s Guide to the Participation of Children and Teens in Medical Education - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Health Research in Children: What Parents Need To Know - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Social Determinants of Health (SDH)
Social determinants of health (SDH): Inquiry about impact of poverty: “Within the past 12 mos, did you worry that your food would run out before you got money to buy more, OR did the food not last and you didn’t have money to get more?” Food insecurity (Pediatrics) | CLEAR tool kit | Poverty Tool (OCFP) | Social determinants of health (CFPC) | Infrastructure to address SDH (PCH) |
Healthy Sleep Habits
Assess healthy sleep habits: Normal sleep (quality and quantity for age) is associated with typical development and leads to better health outcomes. Sleeping Behaviour (EECD). Recommended sleep duration per 24 hrs: 12-14 hrs (infants 4–12 months); 11-14 hrs (1–2 yrs); 10-13 hrs. (3–5 yrs); 9-12 hrs (6–12 yrs); 8-10 hrs (13–18 yrs). Turn off computer/TV screens 60 minutes before bedtime. No computer/TV screens in bedroom. Recommended amount of sleep (AASM) |
Safe Sleep for Babies - Canadian Pediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Healthy Sleep for your Baby and Child - Canadian Pediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Safe Sleep for Your Baby - Public Health Agency of Canada
Home Safety: Bed Time - Parachute Canada
Sleeping Problems - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Night Terrors - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Bedwetting - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Bed-Wetting (Enuresis) - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Sleep: Learning Hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/SLEEP
Family Conflict
Prevention of child maltreatment:
Discuss with parents of preschoolers teaching names of genitalia, appropriate and inappropriate touch, and normal sexual behaviour for age. Exposure to personal violence and other forms of violence has significant impact on physical and emotional well-being of children. Assess home visit need: There is good evidence for home visiting by nurses during the perinatal period through infancy for first-time mothers of low socioeconomic status, single parents or teenaged parents to prevent physical abuse and/or neglect. |
Second-hand smoke exposure
Second-hand smoke/E-cigs/Cannabis exposure: There is no safe level of exposure. Advise caregivers to stop smoking and/or reduce second-hand smoke exposure, which contributes to childhood respiratory illnesses, SIDS and neuro-behavioural disorders. Offer smoking cessation resources. Educate parents on the health risks and harms associated with e-cigs and cannabis (including edibles), and on safe storage. Cannabis (CPS) |
Medications, alcohol and cannabis in breastfeeding - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth. https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=442&language=English
Breastfeeding learning hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth.
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/breastfeeding
Sun exposure/sunscreens/insect repellents
Sun exposure/sunscreens: Minimize sun exposure. Wear protective clothing, hats, properly applied sunscreen with SPF ≥ 30 for those > 6 months of age. Insect bites/repellents: Prevent insect bites. No DEET in < 6 months; 6–24 months 10% DEET apply max once daily; 2–12 years 10% DEET apply max TID. Preventing mosquito and tick bites (CPS) |
Sun Safety - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Sunburn - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Sun: Protecting Your Child’s Skin - The Hosptial for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Keep your young child safe around the house - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Insect repellents: How to protect your child from insect bites - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Insect Bites - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Heat-related Illness: How to Prevent - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=1966&language=English
OTC cough/cold medications
Advise parents against using OTC cough/cold medications: Treating cough and cold (CPS) |
Using Over-The-Counter Drugs to Treat Cold Symptoms - Canadian Paediatric Society– Caring for Kids
Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM)
Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM): Questions should be routinely asked about the use of complementary and alternative medicine, therapy, or products, especially for children with chronic conditions. Natural Health Products (Caring for kids, CPS); Homeopathy (CPS); Chiropractic care (PCH) |
Natural Health Products and Children - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Natural Health Products - Health Canada
Fever advice/thermometers
Fever advice/thermometers: Fever ≥ 38oC in an infant < 3 months needs urgent evaluation. Ibuprofen and acetaminophen are both effective antipyretics. Acetaminophen remains the first choice for antipyresis under 6 months of age; thereafter ibuprofen or acetaminophen may be used. Alternating acetaminophen with ibuprofen for fever control is not recommended in primary care settings as this may encourage fever phobia, and the potential risks of medication error outweigh measurable clinical benefit. Fever in the returning child traveller (CPS) | Fever and temperature taking (Caring for Kids CPS) |
Fever and Temperature Taking - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Temperature Taking - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Fever - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Health conditions and treatments - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Febrile Seizures - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Using Over-The-Counter Drugs to Treat Cold Symptoms - Canadian Paediatric Society– Caring for Kids
Supervised Tummy Time While Awake
Tummy time: Helping your baby - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=296&language=English
Sleep: Learning Hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/SLEEP
Family Healthy Active Living / Sedentary Behaviour / Screen Time
Healthy active living (CPS) | CSEP guidelines | Screen time and young children (CPS) Encourage increased physical activity, with parents as role models, through interactive floor-based play for infants and a variety of activities for young children, and decreased sedentary pastimes.
|
Healthy bodies for children and teens - Dietitians of Canada
Children and Physical Activity - Health Canada
Finding and Keeping a Healthy Body Weight - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
Snowmobiles: Safety Tips for Families - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Cycling: Child carriers and trailers - Parachute Canada
Water Safety for Young Children - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Frostbite - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Winter Safety - Canadian Paedistric Society – Caring for Kids
Winter outdoor safety - Parachute Canada
Playground Safety - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Playgrounds and play spaces - Parachute Canada
Sports – Related Concussions - Canadian Pediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Drowning: Play parks and water features - Parachute Canada
Physical Activity for Children and Youth - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
When is My Child Ready For Sports? - CPS – Caring for Kids
Tips for Raising Kids with Healthy Habits - Dietitians of Canada - UnlockFood.ca https://www.unlockfood.ca/en/Articles/Child-Toddler-Nutrition/Tips-for-Raising-Kids-with-Healthy-Weights.aspx
Dressing for the Cold - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=1940&language=English&hub=wintersafety
Cold Weather Injuries - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=1912&language=English&hub=wintersafety
Heat-related Illness: How to Prevent - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=1966&language=English
Unstructured outdoor play and risky play - Parachute Canada https://www.parachutecanada.org/en/injury-topic/playgrounds-and-play-spaces/unstructured-outdoor-play-and-risky-play/
Helmets: How they Prevent Injury - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=1982&language=English
Sleep: Learning Hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/SLEEP
Sensory development and activities for children older than 2 years - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=3890&language=English
Spatial reasoning skills: How to foster in children - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=649&language=English
Encourage Reading
Encourage parents to read and sing to their infants and children and to limit TV, video and computer games to provide more opportunities for reading. |
Read, Speak, Sing To Your Baby: How Parents Can Promote Literacy from Birth - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Promoting Reading in School-Aged Children - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Early language development in babies and toddlers - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/early-language-development-in-babies-and-toddlers?language=en
Babbling with your child - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=3895&language=English
Tips for developing language at 3 years - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=3897&language=English
Sensory development and activities for children older than 2 years - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=3890&language=English
Spatial reasoning skills: How to foster in children - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=649&language=English
Caring for Kids New to Canada - Canadian Paediatric Society. https://www.kidsnewtocanada.ca/
Child care/return to work
Inquire about current child care arrangements. High quality child care is associated with improved paediatric outcomes in all children. Factors enhancing quality child care include: practitioner general education and specific training; group size and child/staff ratio; licensing and registration/accreditation; infection control and injury prevention; and emergency procedures.
|
Biting in Childcare : What are the Risks? - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Child Care: Making the Best Choice for your Family - Canadian Paediatric Society - Caring for Kids
Teeth
Oral Health - Smiles for Life
|
Pacifiers (Soothers) : A User’s Guide for Parents - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Healthy Teeth for Children - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Dental Care For Children – Cleaning Teeth - Canadian Dental Association
Dental Care For Children – Nutrition for Children - Canadian Dental Association
Dental Care For Children – Dental Development - Canadian Dental Association
Early Childhood Tooth Decay - Canadian Dental Association
Your Child’s First Visit (To The Dentist) - Canadian Dental Association
Dental Care for Children – Fluoride and Your Child - Canadian Dental Association
Dental Care for Children – Pacifiers and Thumb Sucking - Canadian Dental Association
Tooth Injury: First Aid - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Teething - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Teeth: Dental Care for Children - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Caring for Kids New to Canada - Canadian Paediatric Society. https://www.kidsnewtocanada.ca/
Avoid all sweetened fruit drinks
Avoid all sweetened fruit drinks, sport-drinks, energy drinks and soft-drinks; restrict fruit juice consumption to a maximum of 1/2 cup (125 mL) per day. Limit the consumption of prepared food and beverage products that are high in sugar content. Limit/avoid consuming highly processed foods that are high in dietary sodium. Dietary sodium (CPS) |
Avoid honey
Avoid honey until 1 year of age to prevent botulism. |
Breastfeeding learning hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth.
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/breastfeeding
Introduction to solids
Introduction to solids: A few weeks before to just after 6 months, guided by infant’s readiness (CPS Caring for Kids), start iron containing foods to avoid iron deficiency. A variety of soft texture foods, ranging from purees to finger foods, can be introduced. Allergenic foods: For all infants, including those at high risk for allergies, allergenic foods (especially eggs and peanut products) can be introduced with other solids around 6 months, but not before 4 months, as guided by the infant’s signs of readiness. Once allergenic solids are introduced, they should be fed a few times a week to maintain tolerance.
|
Fish consumption: 2 servings/week of low mercury fish: Fish consumption and mercury (HC) |
Iron containing foods
Introduction to solids: A few weeks before to just after 6 months, guided by infant’s readiness (CPS Caring for Kids), start iron containing foods to avoid iron deficiency. A variety of soft texture foods, ranging from purees to finger foods, can be introduced. Allergenic foods: For all infants, including those at high risk for allergies, allergenic foods (especially eggs and peanut products) can be introduced with other solids around 6 months, but not before 4 months, as guided by the infant’s signs of readiness. Once allergenic solids are introduced, they should be fed a few times a week to maintain tolerance.
|
Fish consumption: 2 servings/week of low mercury fish: Fish consumption and mercury (HC) |
Allergenic foods
Fish consumption: 2 servings/week of low mercury fish: Fish consumption and mercury (HC) |
Milk Consumption
Milk consumption range is consensus only & is provided as an approximate guide. Dietary fat content: Restriction of dietary fat during the first 2 years is not recommended since it may compromise the intake of energy and essential fatty acids, required for growth and development. After 2 years, a gradual transition begins from a high fat milk diet to a lower fat milk diet, as per Canada’s Food Guide. |
Independent/self feeding
Promote family meals with independent/self-feeding while offering a variety of healthy foods. NHTI: 6–24 months |
Nutrition for Healthy Term Infants Birth to 6 Months – Health Canada
My Food Guide Serving Tracker for Breastfeeding Women - Health Canada
Simple Lunch Solutions - Dietitians of Canada
Eating Well with Canada’s Food Guide - Health Canada
Say Goodbye to Picky Eating - Dietitians of Canada - UnlockFood.ca. https://www.unlockfood.ca/en/Articles/Child-Toddler-Nutrition/Say-Goodbye-to-Picky-Eating!.aspx
Help! My kids won't eat enough vegetables and fruits. Dietitians of Canada unlockfood.ca: https://www.unlockfood.ca/en/Articles/Child-Toddler-Nutrition/Help!-My-kids-won-t-eat-enough-vegetables-and-fruits.aspx
Tips for Raising Kids with Healthy Habits - Dietitians of Canada - UnlockFood.ca https://www.unlockfood.ca/en/Articles/Child-Toddler-Nutrition/Tips-for-Raising-Kids-with-Healthy-Weights.aspx
Constipation in Children - Dietitians of Canada - UnlockFood.ca https://www.unlockfood.ca/en/Articles/Childrens-Nutrition/Health-Conditions/Constipation-in-Children.aspx
Footwear
Footwear: Shoes are for protection, not correction. Walking barefoot develops good toe gripping and muscular strength. Footwear for children (CPS) |
Footwear for Children - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Tonsil size/sleep-disordered breathing
Tonsil size/sleep-disordered breathing: Screen for sleep problems. Behavioural sleep problems and snoring in the presence of sleep-disordered breathing warrants assessment re obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). OSA (AAP) |
Sleep: Learning Hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/SLEEP
Blood lead if at risk
Lead: There is no safe level of lead exposure in children. Evidence suggests that low blood lead levels can have adverse health effects on a child’s cognitive function. Blood Lead Screening is recommended for children who:
|
Lead Poisoning - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Caring for Kids New to Canada - Canadian Paediatric Society. https://www.kidsnewtocanada.ca/
Pesticides
Pesticides: Ask about pesticide use and storage at home; avoid exposure. Wash all fruits and vegetables that cannot be peeled. Food additives and child health (AAP) | Pesticide Exposure in Children (AAP) |
Fontanelles
Fontanelles: The posterior fontanelle is usually closed by 2 months and the anterior by 18 months. The Abnormal fontanel (AAFP) |
Eyes (red reflex)
Vision inquiry/screening: Vision screening (CPS)
|
Vision Screening
Vision inquiry/screening: Vision screening (CPS)
|
Caring for Kids New to Canada - Canadian Paediatric Society. https://www.kidsnewtocanada.ca/
Hearing inquiry/screening
Hearing inquiry/screening: Language delay or parental concerns about hearing acuity should prompt a rapid referral for hearing assessment. Formal audiology testing should be performed in all high-risk infants, including those with normal UNHS. Older children should be screened if clinically indicated. |
Your Baby’s Hearing - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Caring for Kids New to Canada - Canadian Paediatric Society. https://www.kidsnewtocanada.ca/
Your Newborn: Bringing Baby Home - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Hips
Hips: There is insufficient evidence to recommend routine diagnostic imaging for screening for developmental dysplasia of the hips, but examination of the hips should be included until at least one year, or until the child can walk. Exam includes assessing limb length discrepancy and asymmetric thigh or buttock (gluteal) creases; performing Ortolani manoeuvre (usually negative after 3 mos); and testing for limited abduction (usually positive after 3 mos). Consider selective imaging between 6 wks and 6 mos if risk factor (i.e. breech, family history, hip instability on physical exam). DDH (AAP) |
Muscle tone
Muscle tone: Assessment should be performed for abnormal tone or deep tendon reflexes, or for asymmetric movements (moving one side more than other). These may be early signs of cerebral palsy or neuromotor disorder and suggest the need for further assessment. CP Features (DM&CN) |
Spine/Anus
Jaundice
Jaundice: Bilirubin testing (total and conjugated) if persists beyond 2 wks of age. Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia Guidelines (CPS) | Newborn screening for biliary atresia (AAP). |
Bruising
Bruising: Unexplained bruising warrants evaluation re child maltreatment or medical illness. |
Neck/torticollis
| Check neck for torticollis. |
Tummy time: Helping your baby - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=296&language=English
Tongue Mobility
Inspect tongue mobility for ankyloglossia if breastfeeding problems. Ankyloglossia and breastfeeding (CPS) |
Hemoglobinopathy screening
Hemoglobinopathy screening: Screen all neonates from high-risk groups: Asian, African & Mediterranean. |
Universal newborn hearing screening
Universal newborn hearing screening (UNHS): Effectively identifies infants with congenital hearing loss and allows for early intervention & improved outcomes. Universal newborn hearing screening (CPS) |
Newborn Screening Tests - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Your Newborn: Bringing Baby Home - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Teeth/Caries Risk
Dental: Examine for problems including caries, oral soft tissue infections or pathology; and for normal teeth eruption sequence. Canadian Caries Risk Assessment Tool 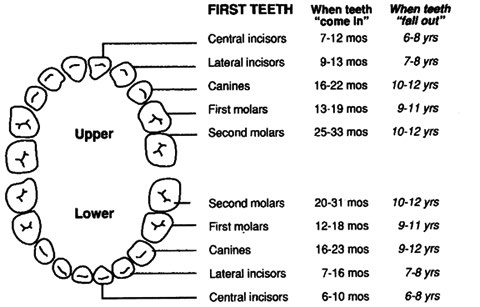 |
Nonparental Child Care
NONPARENTAL CHILD CARE Inquire about current child care arrangements. High quality child care is associated with improved paediatric outcomes in all children. Factors enhancing quality child care include: practitioner general education and specific training; group size and child/staff ratio; licensing and registration/accreditation; infection control and injury prevention; and emergency procedures.
|
Hepatitis B vaccine (Hep B)
Hepatitis B vaccine (Hep B):
|
Immunization information - Immunize Canada. https://www.immunize.ca/
Caring for Kids New to Canada - Canadian Paediatric Society. https://www.kidsnewtocanada.ca/
Hepatitis B Vaccine - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Injury Prevention
INJURY PREVENTION: In Canada, unintentional injuries are the leading cause of death in children and youth. Most of these preventable injuries are caused by motor vehicle collisions, suffocation, drowning, fire, poisoning, and falls. Injury deaths in Canada (PHAC). Unexplained injuries (e.g. fractures, bruising, burns) or injuries that do not fit the rationale provided or developmental stage raise concern for child maltreatment. |
Food Poisoning: Protecting Your Family - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Food Safety for Pregnant Women - Health Canada – It’s Your Health
Food Safety at Home - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Halloween Safety - Health Canada – It’s Your Health
Pacifiers (Soothers) : A User’s Guide for Parents - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Car Seat Safety - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Car Seats - Parachute Canada
Choosing the right car seat - Parachute Canada
Car seats: Other ways to travel - Parachute Canada
All-Terrain Vehicle Safety - Parachute Canada
Are ATVs safe for children and youth? - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Snowmobiles: Safety Tips for Families - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Cycling: Child carriers and trailers - Parachute Canada
Helmets - Parachute Canada
Drowning - Parachute Canada
Water Safety for Young Children - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Water safety and drowning prevention - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Choking - Parachute Canada
Choking: First Aid - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Sun Safety - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Sunburn - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Sun: Protecting Your Child’s Skin - The Hosptial for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Burns and scalds - Parachute Canada
Preventing burns: Winter safety - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Burns: Learning hub - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Preventing Burns: Campfires and Fireworks - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Burns: Household Safety and Prevention - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Bathtub Safety - Parachute Canada
Frostbite - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Winter Safety - Canadian Paedistric Society – Caring for Kids
Winter outdoor safety - Parachute Canada
Poisoning - Parachute Canada
Poison Information Centers in Canada - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Poison-Proof Your Home: A Guide to Keeping Your Family Safe From Poisons - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Lead Poisoning - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Home Safety: Around the House - Parachute Canada
Are Trampolines Safe? - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Playground Safety - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Playgrounds and play spaces - Parachute Canada
Sports – Related Concussions - Canadian Pediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Title: Is Your Child Safe? - Source: Health Canada
Safe Sleep for Babies - Canadian Pediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Preventing Flat Heads in Babies Who Sleep on Their Backs - Canadian Pediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Healthy Sleep for your Baby and Child - Canadian Pediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Safe Sleep for Your Baby - Public Health Agency of Canada
Home Safety: Bed Time - Parachute Canada
Sleeping Problems - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Keep your young child safe around the house - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Gun Safety: Information for Families - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Children and pets: Tips for Bringing Pets into your Home - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Drowning: Play parks and water features - Parachute Canada
Your Preschooler and Safety: How to Prevent Injuries at Home - Canadian Paediatric Society - Caring for Kids
When is My Child Ready For Sports? - CPS – Caring for Kids
Drowning: Backyard pools - Parachute Canada https://www.parachutecanada.org/en/injury-topic/drowning/backyard-pools/
Drowning: Lifejackets and PFDs - Parachute Canada https://www.parachutecanada.org/en/injury-topic/drowning/lifejackets-and-personal-flotation-devices-pfds/
Dressing for the Cold - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=1940&language=English&hub=wintersafety
Cold Weather Injuries - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=1912&language=English&hub=wintersafety
Heat-related Illness: How to Prevent - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=1966&language=English
Prevent Child Deaths in Hot Cars - American Academy of Pediatrics - healthychildren.org https://www.healthychildren.org/English/safety-prevention/on-the-go/Pages/Prevent-Child-Deaths-in-Hot-Cars.aspx
Unstructured outdoor play and risky play - Parachute Canada https://www.parachutecanada.org/en/injury-topic/playgrounds-and-play-spaces/unstructured-outdoor-play-and-risky-play/
Head Injury and concussion - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=766&language=English
Helmets: How they Prevent Injury - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=1982&language=English
Sleep: Learning Hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/SLEEP
Industry Guide for the Classification of Cribs, Cradles, Bassinets and Related Products - Health Canada https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/consumer-product-safety/reports-publications/industry-professionals/industry-guide-classification-cribs-cradles-bassinets-related-products.html
Caring for Kids New to Canada - Canadian Paediatric Society. https://www.kidsnewtocanada.ca/
Biting in Childcare : What are the Risks? - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Animal Bites: First Aid - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Needle Stick Injuries - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Your Newborn: Bringing Baby Home - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Environmental Health
Websites about environmental issues:
|
Nutrition
NUTRITION: Nutrition for healthy term infants (NHTI): 0–6 months | 6–24 months | NutriSTEP® | Overview NHTI 0–6 months (CPS) | 2019 Nutrition Guidelines (ODPH) | Dietitians of Canada |
Nutrition for Healthy Term Infants Birth to 6 Months – Health Canada
Healthy bodies for children and teens - Dietitians of Canada
Drugs and Lactation Database (TOXNET) - A peer-reviewed and fully referenced database of drugs to which breastfeeding mothers may be exposed - National Institute of Health
Finding and Keeping a Healthy Body Weight - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
Healthy Eating for Children - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Healthy Snacks for Children - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Appetite Slump in Toddlers - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
When your Child is a Picky Eater - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Breastfeeding - Canadian Paediatric Society - Caring for Kids
Children's Nutrition - Dietitians of Canada
Breastfeeding - La Leche League Canada
Breastfeeding and Infant Nutrition - Public Health Agency of Canada
Breastfeeding: How do you know your baby is getting enough milk? - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Breastfeeding Your Baby – More Information - Baby Friendly NL, Health Canada
Iron Needs of Babies and Children - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Breastfeeding problems: Sore nipples - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
Prebiotics and Probiotics - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
High Fibre Diet - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
My Food Guide Serving Tracker for Breastfeeding Women - Health Canada
Healthy Bowel Habits for Children - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Excessive Gas (Flatulence) - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Constipation - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Diarrhea - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Food Poisoning: Protecting Your Family - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Vitamin D Supplementation and Breastfeeding - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Food Safety for Pregnant Women - Health Canada – It’s Your Health
Food Safety at Home - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Halloween Safety - Health Canada – It’s Your Health
Food Allergies and Intolerances - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Allergies - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Pacifiers (Soothers) : A User’s Guide for Parents - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Food Allergies and Travelling - HSC – AboutKidsHealth
Pediatric Nutrition Guidelines (Birth to Six Years) for Health Professionals - Ontario Dietitians in Public Health (ODPH)
Breastfeeding: Weaning and withdrawing your milk supply - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Simple Lunch Solutions - Dietitians of Canada
Eating Well with Canada’s Food Guide - Health Canada
Feeding Your Baby in the First Year - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Choking - Parachute Canada
NutriStep®: Nutrition Screening Tool for Toddlers and Preschoolers - Sudbury and District Health Unit
Nutrition Labels: Finding Out About The Food You Eat - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Dental Care For Children – Nutrition for Children - Canadian Dental Association
Early Childhood Tooth Decay - Canadian Dental Association
Medications, alcohol and cannabis in breastfeeding - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth. https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=442&language=English
Breastfeeding learning hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth.
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/breastfeeding
Say Goodbye to Picky Eating - Dietitians of Canada - UnlockFood.ca. https://www.unlockfood.ca/en/Articles/Child-Toddler-Nutrition/Say-Goodbye-to-Picky-Eating!.aspx
Help! My kids won't eat enough vegetables and fruits. Dietitians of Canada unlockfood.ca: https://www.unlockfood.ca/en/Articles/Child-Toddler-Nutrition/Help!-My-kids-won-t-eat-enough-vegetables-and-fruits.aspx
Tips for Raising Kids with Healthy Habits - Dietitians of Canada - UnlockFood.ca https://www.unlockfood.ca/en/Articles/Child-Toddler-Nutrition/Tips-for-Raising-Kids-with-Healthy-Weights.aspx
Constipation in Children - Dietitians of Canada - UnlockFood.ca https://www.unlockfood.ca/en/Articles/Childrens-Nutrition/Health-Conditions/Constipation-in-Children.aspx
Caring for Kids New to Canada - Canadian Paediatric Society. https://www.kidsnewtocanada.ca/
Your Newborn: Bringing Baby Home - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Development
Manoeuvres are based on evidence-based literature on milestone acquisition. Evidence-based milestone ages (PCH). They are not a developmental screen, but rather an aid to developmental surveillance. They are set after the time of typical milestone acquisition. Thus, absence of any one or more items is considered a high-risk marker and indicates consideration for further developmental assessment, as does parental or caregiver concern about development at any stage. Assessment tools Table 4 (CPS) | Global Delay (CPS)
|
Your Child’s Development – What to Expect - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Bedwetting - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Bed-Wetting (Enuresis) - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Autism spectrum disorder: What you need to know - Canadian Paediatric Society - Caring for Kids. https://www.caringforkids.cps.ca/handouts/behavior-and-development/autism-spectrum-disorder-what-you-need-to-know
Early language development in babies and toddlers - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/early-language-development-in-babies-and-toddlers?language=en
Babbling with your child - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=3895&language=English
Tips for developing language at 3 years - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=3897&language=English
Sensory development and activities for children older than 2 years - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=3890&language=English
Spatial reasoning skills: How to foster in children - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=649&language=English
Caring for Kids New to Canada - Canadian Paediatric Society. https://www.kidsnewtocanada.ca/
Immunizations
|
Provincial & territorial routine & catch-up vaccination schedule for infants & children in Canada - Public Health Agency of Canada
A Parent’s Guide to Immunization Information on the Internet - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Vaccination and Your Child - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
A Parent's guide to Vaccination - Public Health Agency of Canada
Vaccine Safety: Canada's system - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Your Immunization Schedule – Immunization Schedule Tool - Public Health Agency of Canada
Immunization “Catch Up” for Children Who Have Not Been Fully Immunized - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
Needle pokes: Reducing pain in infants aged up to 18 months - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Needle pokes: Reducing pain in children aged 18 months or over - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Vaccine safety, surveillance and reporting - Health Canada
https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/immunization/vaccine-safety.html
Immunization information - Immunize Canada. https://www.immunize.ca/
Vaccines for Children: Deciding to vaccinate - Health Canada.
https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/vaccination-children.html
Caring for Kids New to Canada - Canadian Paediatric Society. https://www.kidsnewtocanada.ca/
Immunization Schedule - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Vaccine Safety Net - World Health Organization
HPV: What teens need to know - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Hemoglobin
Anemia screening: Screening for iron deficiency anemia should be considered between 6 and 18 months of age for infants/children from high risk groups: E.g. Low SES; Indigenous communities; newly arrived refugee, internationally adopted and immigrant children from resource-poor countries; low-birth-weight and premature infants; infants/children fed whole cow’s milk before 9 months of age or at quantities > 500 mls/day; prolonged bottle feeding beyond 15 months of age; or sub-optimal intake of iron-containing foods. Beyond this age, anemia screening as per additional risk factors. Iron requirements (CPS) |
Caring for Kids New to Canada - Canadian Paediatric Society. https://www.kidsnewtocanada.ca/
Tuberculosis – TB skin testing
Tuberculosis – TB skin testing: For up-to-date information, see Canadian TB Standards: 2014 |
Toilet Learning
The process of toilet learning has changed significantly over the years and within different cultures. In Western culture, a child-centred approach is recommended, where the timing and methodology of toilet learning is individualized as much as possible. Toilet learning (CPS) |
Abnormal-Looking Stool - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Bedwetting - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Bed-Wetting (Enuresis) - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Toilet Learning - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Toilet Training - The Hospital for Sick Children – AboutKidsHealth
Handwashing for Parents and Kids - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Canada’s Food Guide
Canada’s Food Guide: Health Canada’s guidelines and considerations on healthy eating |
Say Goodbye to Picky Eating - Dietitians of Canada - UnlockFood.ca. https://www.unlockfood.ca/en/Articles/Child-Toddler-Nutrition/Say-Goodbye-to-Picky-Eating!.aspx
Help! My kids won't eat enough vegetables and fruits. Dietitians of Canada unlockfood.ca: https://www.unlockfood.ca/en/Articles/Child-Toddler-Nutrition/Help!-My-kids-won-t-eat-enough-vegetables-and-fruits.aspx
Tips for Raising Kids with Healthy Habits - Dietitians of Canada - UnlockFood.ca https://www.unlockfood.ca/en/Articles/Child-Toddler-Nutrition/Tips-for-Raising-Kids-with-Healthy-Weights.aspx
Dietary fat content
Dietary fat content: Restriction of dietary fat during the first 2 years is not recommended since it may compromise the intake of energy and essential fatty acids, required for growth and development. After 2 years, a gradual transition begins from a high fat milk diet to a lower fat milk diet, as per Canada's Food Guide. Promote family meals with independent/self-feeding while offering a variety of healthy foods. NHTI: 6-24 months |
Children's Nutrition - Dietitians of Canada
Breastfeeding learning hub - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth.
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/breastfeeding
Bicycle
Bicycle: wear bike helmets and advocate for helmet legislation for all ages. Replace if heavy impact or damage. Bicycle helmet legislation (CPS) |
All-Terrain Vehicle Safety - Parachute Canada
Cycling: Child carriers and trailers - Parachute Canada
Helmets - Parachute Canada
Sports – Related Concussions - Canadian Pediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Keep your young child safe around the house - Canadian Paediatric Society – Caring for Kids
Head Injury and concussion - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=766&language=English
Helmets: How they Prevent Injury - The Hospital for Sick Children - AboutKidsHealth
https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/Article?contentid=1982&language=English
Social/Emotional - Communications Skills
Specific screening for ASD at 18–24 months should be performed on all children with any of the following risk factors: failed items on the social/emotional/communication skills inquiry, sibling with autism, or developmental concern by parent, caregiver, or physician. Increased prevalence for ASD is also associated with prematurity, and certain chromosomal, genetic and neurological disorders. Standardized, evidence-based screening tools for detection of early ASD symptoms should be used as per guidelines. ASD (CPS): Early detection | Diagnostic assessment | Management | M-CHAT™ |
Autism spectrum disorder: What you need to know - Canadian Paediatric Society - Caring for Kids. https://www.caringforkids.cps.ca/handouts/behavior-and-development/autism-spectrum-disorder-what-you-need-to-know
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure: Check BP at all visits for those at risk > 3 yrs old. Some risk factors: obesity, sleep-disordered breathing, prematurity, renal disease, congenital heart disease, diabetes, or on med’ns that ^ BP. |
