
Fontanelles: The posterior fontanelle is usually closed by 2 months and the anterior by 18 months.
The Abnormal fontanel (AAFP)
Vision inquiry/screening: Vision screening (WHO pocket book)
- Check red reflex for serious ocular diseases such as retinoblastoma and cataracts.
- Corneal light reflex/cover–uncover test & inquiry for strabismus: With the child focusing on a light source, the light reflex on the cornea should be symmetrical. Each eye is then covered in turn, for 2–3 seconds, and then quickly uncovered. The test is abnormal if the uncovered eye “wanders” OR if the covered eye moves when uncovered.
- Check visual acuity at age 3–5 years.
Hearing inquiry/screening: Language delay or parental concerns about hearing acuity should prompt a rapid referral for hearing assessment. Formal audiology testing should be performed in all high-risk infants, including those with normal UNHS. Older children should be screened if clinically indicated. Hearing assessment beyond neonatal screening (AAP)
Inspect tongue mobility for ankyloglossia if breastfeeding problems. Ankyloglossia and breastfeeding (CPS)
Tonsil size/sleep-disordered breathing: Screen for sleep problems. Behavioural sleep problems and snoring in the presence of sleep-disordered breathing warrants assessment re: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
2012 AAP OSA Guidelines
Muscle tone/Persistence of developmental (primitive) reflexes: Assessment should be performed for abnormal tone or deep tendon reflexes, or for asymmetric movements (moving one side more than other) as well as for the persistence of developmental reflexes (e.g. Moro, asymmetric tonic neck, palmar grasp) beyond 5-6 months. These may be early signs of cerebral palsy or neuromotor disorder and suggest the need for further assessment.
Neonatal brachial plexus palsy (CPS)
Childhood Disability LINK: Early detection of CP Prompts for referral
Hips: There is insufficient evidence to recommend routine diagnostic imaging for screening for developmental dysplasia of the hips, but examination of the hips should be included until at least one year, or until the child can walk. Exam includes assessing limb length discrepancy and asymmetric thigh or buttock (gluteal) creases; performing the Ortolani manoeuvre for hip instability in the first 3 mos, then testing for limited or asymmetric hip abduction until 12 months. Consider selective imaging between 6 wks and 6 mos for infants with normal hip exam if breech or family history, and for all infants with positive findings on P/E.
DDH (AAP)
Check palate for cleft Cleft lip/palate (AAP)
Spine/Anus: Examine spine for cutaneous signs of occult spinal dysraphism. Check anal patency.
Congenital Brain and Spinal Cord Malformations (AAP)
Umbilicus: Gently pat dry and review S&S of infection.
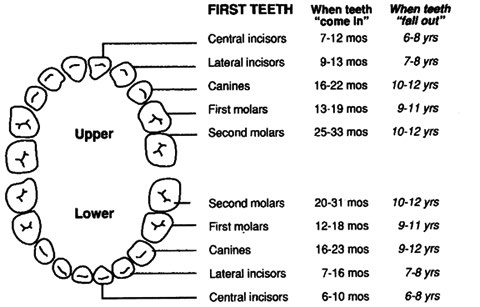
Dental: Examine for problems including caries, oral soft tissue infections or pathology; and for normal teeth eruption sequence.
Canadian Caries Risk Assessment Tool
Sentinel injuries (such as bruising, subconjunctival hemorrhages, or intra-oral trauma to the frenulum, lips, oral mucosa, gingiva or tongue) or other unexplained injuries warrant evaluation re: child maltreatment or medical illness.
Sentinel injuries (Ped Rad) Bruising in suspected maltreatment cases (CPS)
Jaundice: Bilirubin testing (total and conjugated) if persists beyond 2 wks of age. Acholic stools and prolonged jaundice (predominantly conjugated) can be signs of biliary atresia.
Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia Guidelines (CPS) Screening for biliary atresia (CFP)
Check neck for torticollis. Congenital muscular torticollis (Ped)
Blood pressure: Check BP at all visits for those at risk > 3 yrs old. Some risk factors: obesity, sleep-disordered breathing, prematurity, renal disease, congenital heart disease, diabetes, or on medications that increase BP. High blood pressure in children, including definitions:
